1. What is Chorionic villous sampling (CVS)?
CVS is an invasive prenatal diagnosis procedure aiming to obtain a small sample of the placental tissue (chorionic villi) (see photo). The procedure is usually performed between 11- 14 weeks of gestation.
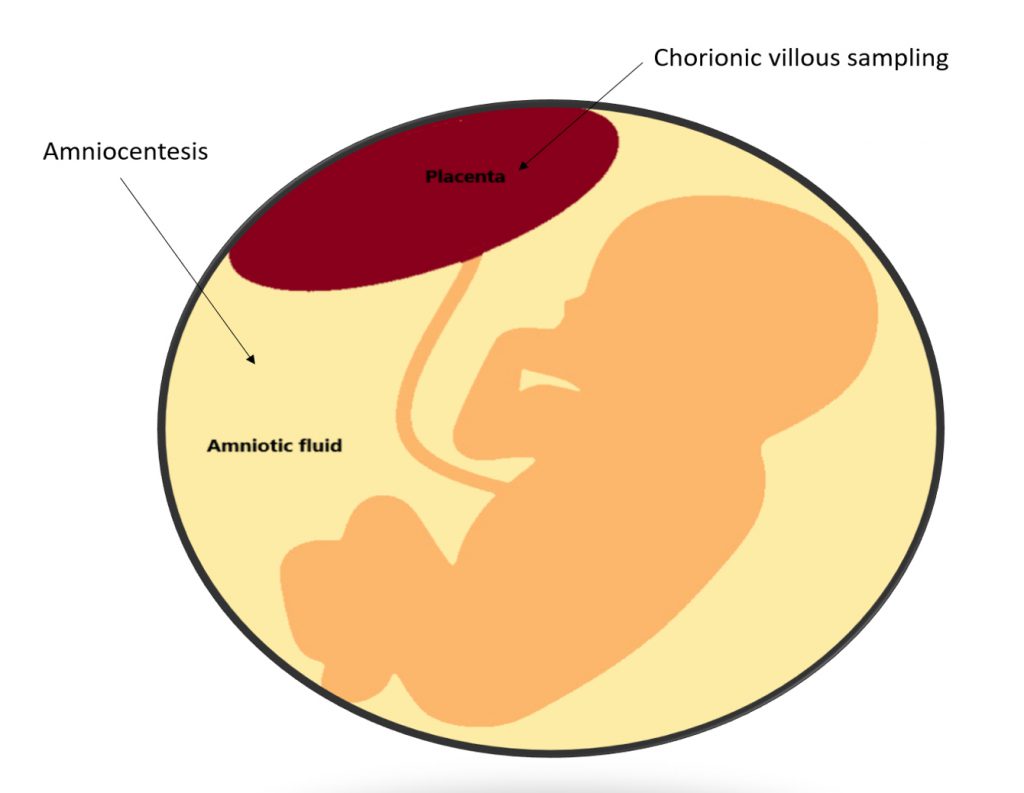
2. How is CVS carried out?
CVS is an outpatient procedure. An ultrasound examination is first performed to locate the site of the placenta. Then a local anaesthetic medication is injected to the mother’s tummy. After the medication has taken effect, a fine needle is passed under ultrasound guidance through the mother’s tummy and uterus to the placenta. A small sample of tissue is obtained by suction. The sampling procedure takes only a few minutes. The mother can go home after the procedure.
3. What is amniocentesis?
Amniocentesis is an invasive prenatal diagnosis procedure aiming to obtain a small sample of amniotic fluid from the mother’s uterus (see photo). Amniotic fluid is the watery fluid that surrounds the fetus and it contains cells that the fetus has shed. The procedure is usually performed between 16-20 weeks of gestation.
4. How is amniocentesis carried out?
Amniocentesis is an outpatient procedure. An ultrasound examination is first performed to locate the best site for sampling. Then a fine needle is passed through the mother’s tummy into the amniotic fluid cavity and a small amount of the fluid is withdrawn. The sampling process takes around 1 minute.
5. What can the samples be sent for?
The chorionic villi or the amniotic fluid can be sent for examination of the chromosomal constitution and genetic tests.
6. What are the risks of the procedures?
Both are safe procedures in general although they carry a small miscarriage rate, in the order of 0.3-0.5%. Other complications such as wound infection, uterine infection, haemorrhage, amniotic fluid leakage and failed procedure are very rare.
